Note: This is a project under development. The articles on this wiki are just being initiated and broadly incomplete. You can Help creating new pages.
Difference between revisions of "Prosopis cineraria - Indian mesquite"
(→External Links) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
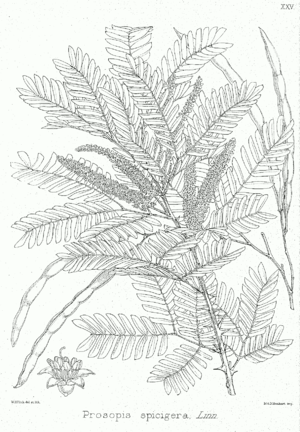
'''Shami''' is a moderate sized throny tree with bipinnate leaves distributed from Iran to India. Within India, it is found in the dry and arid regions on the alluvial plains. | '''Shami''' is a moderate sized throny tree with bipinnate leaves distributed from Iran to India. Within India, it is found in the dry and arid regions on the alluvial plains. | ||
| − | + | ==Uses== | |
| − | ==Uses== | ||
{{Uses|Skin diseases}}, {{Uses|Cysts and tumours}}, {{Uses|Cough}}, {{Uses|Bronchitis and Asthma}}, {{Uses|Piles}}, {{Uses|Dysentery}}, {{Uses|Diarrhea}} | {{Uses|Skin diseases}}, {{Uses|Cysts and tumours}}, {{Uses|Cough}}, {{Uses|Bronchitis and Asthma}}, {{Uses|Piles}}, {{Uses|Dysentery}}, {{Uses|Diarrhea}} | ||
<ref name="Uses"/> | <ref name="Uses"/> | ||
Revision as of 15:15, 5 June 2019
Shami is a moderate sized throny tree with bipinnate leaves distributed from Iran to India. Within India, it is found in the dry and arid regions on the alluvial plains.
Contents
- 1 Uses
- 2 Parts Used
- 3 Chemical Composition
- 4 Common names
- 5 Properties
- 6 Habit
- 7 Identification
- 8 List of Ayurvedic medicine in which the herb is used
- 9 Where to get the saplings
- 10 Mode of Propagation
- 11 How to plant/cultivate
- 12 Commonly seen growing in areas
- 13 Photo Gallery
- 14 References
- 15 External Links
Uses
Skin diseases, Cysts and tumours, Cough, Bronchitis and Asthma, Piles, Dysentery, Diarrhea [1]
Parts Used
Chemical Composition
Common names
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Kannada | banni mara, perumbe |
| Hindi | khejri, sami, chonkar, jhand |
| Malayalam | paramba |
| Tamil | parambai, Vanni, kulivam, tamali |
| Telugu | Jammi, priyadarshini, chamee |
| Marathi | NA |
| Gujarathi | NA |
| Punjabi | NA |
| Kashmiri | NA |
| Sanskrit | Shami, shiva, lakshmi ,mangalya, shankhuphala, Saktuphala, |
| English | Shami tree |
Properties
Reference: Dravya - Substance, Rasa - Taste, Guna - Qualities, Veerya - Potency, Vipaka - Post-digesion effect, Karma - Pharmacological activity, Prabhava - Therepeutics.
Dravya
Rasa
Kashaya (AStringent), Madhura (Sweet)
Guna
Laghu (Light), Rooksha (Dry)
Veerya
Sheeta (cold)
Vipaka
Katu (Pungent)
Karma
Pitta, Kapha
Prabhava
Habit
Identification
Leaf
| Kind | Shape | Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Bipinnate | alternate | Leaves 1-3-jugate, glabrous or puberulous; petiole and rachis 0.5-4 cm long, the pinnae 2-7 cm long; leaflets 7-14-jugate, ovate, straight to subfalcate, without nerves (or 2-4-nerved at base, the midrib excentric), mucronate, 4-15 mm long x 2-4.5 mm broad, greyish when dry; stipules foliaceous, deciduous. |
Flower
| Type | Size | Color and composition | Stamen | More information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bisexual | spiciform racemes | Pale yellow | 5-13 cm long, several together, subpaniculate; peduncle with amplexicaul bract (or 2 bracts united), this caducous and leaving an oblique scar, 1.5-2 mm long; bractlets ovate, sessile, 0.5-0.8 mm long, caducous; pedicels 0.5 mm, to 1.5 mm long when mature; flowers yellow, glabrous; calyx truncate, 0.8-1.2 mm long; corolla 3.5 mm long, glabrous, the petals rolled back in age; anthers 0.8-1 mm long; pistil
glabrous. |
Fruit
| Type | Size | Mass | Appearance | Seeds | More information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A Pod | 8 - 9 cm long | Fruit slender, elongate, 8-19 cm long (including the stipe 0.8-2 cm), subcylindric-torulose, 4-7 mm in diameter, glabrous; pericarp thin, brittle; endocarp segments thin, longitudinal, little developed; seeds distant, longitudinal, ovate, 6 mm long, the tegument with open horse-shoe fissural line on faces, 10-15 in a pod, brown. | seeds 6-15, 8-10 x 7-9 mm, glossy, red | {{{6}}} |
Other features
List of Ayurvedic medicine in which the herb is used
Where to get the saplings
Mode of Propagation
How to plant/cultivate
Season to grow
Soil type
Propagation
Commonly seen growing in areas
Photo Gallery
References
External Links
Categories:
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Skin diseases
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Cysts and tumours
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Cough
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Bronchitis and Asthma
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Piles
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Dysentery
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Diarrhea
- Herbs with Bark used in medicine
- Herbs with Fruits used in medicine
- Herbs with common name in Kannada
- Herbs with common name in Hindi
- Herbs with common name in Malayalam
- Herbs with common name in Tamil
- Herbs with common name in Telugu
- Herbs with common name in Sanskrit
- Herbs with common name in English
- Habit - Tree
- Index of Plants which can be propagated by Seeds
- Index of Plants which can be propagated by Cuttings
- Herbs that are commonly seen in the region of Tropical area
- Herbs
- Fabaceae
- Ayurvedic herbs that don't have seed photos