Note: This is a project under development. The articles on this wiki are just being initiated and broadly incomplete. You can Help creating new pages.
Difference between revisions of "Plant Identification"
(Created page with "To properly identify a plant, the whole plant has to be carefully observed. The physical form and external structure have to be studied to see what categories the plant fits i...") |
(→Inflorescence) |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | To properly identify a plant, the whole plant has to be carefully observed. The physical form and external structure have to be studied to see what categories the plant fits into. These are the features that need to be observed | + | To properly identify a plant, the whole plant has to be carefully observed. The physical form and external structure have to be studied to see what categories the plant fits into. These are the features that need to be observed. |
| − | + | == Habit (form) == | |
| − | *Herb | + | |
| − | Plants that have non-woody stems. Herbs can be annuals or perennials | + | *Herb: Plants that have non-woody stems. Herbs can be annuals or perennials |
| − | *Shrub | + | |
| − | Woody plants that are less than 6m tall and have multiple stems. Shrubs are perennials. | + | *Shrub: Woody plants that are less than 6m tall and have multiple stems. Shrubs are perennials. |
| − | *Tree | + | |
| − | Perennial woody plants with an elongated trunk with leafy branches at the top. | + | *Tree: Perennial woody plants with an elongated trunk with leafy branches at the top. |
| − | *Climber | + | |
| − | Plants with stems that are unable to stand erect, and use trees and other objects to climb up. There are herbaceous as well as woody climbers ([[lianas]]) | + | *Climber: Plants with stems that are unable to stand erect, and use trees and other objects to climb up. There are herbaceous as well as woody climbers ([[lianas]]) |
== Leaf type == | == Leaf type == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*Simple | *Simple | ||
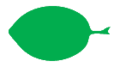
A leaf that has an undivided blade. The leaf may be lobed but does not form distinct leaflets. | A leaf that has an undivided blade. The leaf may be lobed but does not form distinct leaflets. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology attachment petiolate.png|Simple leaf | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
*Compound | *Compound | ||
| Line 22: | Line 25: | ||
*Pinnate (odd): Leaflets are attached along the rachis; there is a terminal leaflet and therefore an odd number of leaflets. | *Pinnate (odd): Leaflets are attached along the rachis; there is a terminal leaflet and therefore an odd number of leaflets. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology odd pinnate.png|Imparipinnate leaf | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
*Pinnate (even): Leaflets are attached along the rachis; there is no terminal leaflet and therefore an even number of leaflets. | *Pinnate (even): Leaflets are attached along the rachis; there is no terminal leaflet and therefore an even number of leaflets. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology even pinnate.png|Paripinnate leaf | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Bipinnate: Leaflets that are further subdivided in a unipinnate arrangement. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology type bipinnately-compound.png|Bipinnate leaf | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | **Tripinnate: Leaflets that are further subdivided in a bipinnate arrangement. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology tripinnate.png|Tripinnate | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | *Trifoliate: A compound leaf made up of three leaflets. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology trifoliolate.png|Trifoliate leaf | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Palmate/Digitate: A type of compound leaf in which the leaflets all originate from the same point, like the fingers from the palm of the hand.| | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology type palmately-compound.png|Palmate leaf | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | A way to distinguish simple leaves from compound leaves is to check for axillary buds. Only simple leaves would have an axillary bud. Pinnate leaves will not have them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Leaf arrangement == | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Alternate: One leaf attached at a node, arranged alternately on the stem. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Ulistnienie (Phyllotaxys alternate.svg}|Alternate | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Opposite: A pair of leaves attached at a node, arranged oppositely. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Ulistnienie (Phyllotaxys opposite-decussate).svg|Opposite | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | *Whorled: Three or more leaves attached at a node, in a radial manner. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology whorled.png|Whorled | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Basal Rosette: Some plants keep their leaves in a tight rosette close to the ground, where the leaves all seem to radiate from a common point. This may be one stage in the life of the plant or it may spend its whole life in that form. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Parthenium hysterophorus plant with flowers.jpg | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Leaf Shape == | ||
| + | Leaves come in a variety of shapes and sizes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology acuminate.png|Acuminate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology aristate.png|Aristate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology cordate.png|Cordate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology cuneate.png|Cuneate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology deltate.png|Deltate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology deltoid.png|Deltoid | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology digitate.png|Digitate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology elliptic.png|Elliptic | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology ensiforme.PNG|Ensiforme | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology falcate.png|Falcate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology flabelate.png|Flabelate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology hastate.png|Hastate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology lanceolate.png|Lanceolate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology linear.png|Linear | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology lobed.png|Lobed | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology multifide.svg|Multifide | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology obcordate.png|Obcordate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology oblanceolate.png|Oblanceolate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology oblong.png|Oblong | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology obovate.png|Obovate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology obtuse.png|Obtuse | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology orbicular.png|Orbicular | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology ovale.png|Ovale | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology pandurate.png|Pandurate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology pedate.png|Pedate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology peltate.png|Peltate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology pinnatisect.png|Pinnatisect | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology posture plicate.png|Plicate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology reniform.png|Reniform | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology rhombic.png|Rombic | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology spatulate.png|Spatulate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology truncate.png|truncate | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Leaf attachment == | ||
| + | The point of attachment of a leaf to a stem. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology attachment amplexicaul.png|Amplexicaule | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology attachment decurrent.png|Decurrent | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology ocrea.svg|Ochreate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology attachment perfoliolate.png|Perfoliate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology attachment petiolate.png|Petiolate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology attachment sessile.png|Sessile | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology attachment sheathing.png|Sheathing | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | == Leaf margin == | |
| − | + | A leaf can be entire (one with a smooth edge) or it can be of the following types. | |
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology crenate.png|crenate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology crenulate.png|crenulate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology dentate-2.png|dentate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology denticulate.png|denticulate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology undulate.png|undulate | ||
| + | File:Leaf morphology serrate.png|serrate | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Inflorescence == | |
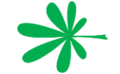
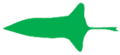
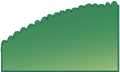
| + | The grouping or cluster of flowers on a branch or a network of branches. | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | File:Tros.jpg|Raceme | ||
| + | File:Tuil.jpg|Corymb | ||
| + | File:Scherm.jpg|Umbel | ||
| + | File:Hoofdje.jpg|Head | ||
| + | File:Kegelvormig hoofdje.jpg|Head | ||
| + | File:Pluim.jpg|Panicle | ||
| + | File:Gevorkt bijscherm.jpg|Cyme | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:35, 10 April 2019
To properly identify a plant, the whole plant has to be carefully observed. The physical form and external structure have to be studied to see what categories the plant fits into. These are the features that need to be observed.
Contents
Habit (form)
- Herb: Plants that have non-woody stems. Herbs can be annuals or perennials
- Shrub: Woody plants that are less than 6m tall and have multiple stems. Shrubs are perennials.
- Tree: Perennial woody plants with an elongated trunk with leafy branches at the top.
- Climber: Plants with stems that are unable to stand erect, and use trees and other objects to climb up. There are herbaceous as well as woody climbers (lianas)
Leaf type
- Simple
A leaf that has an undivided blade. The leaf may be lobed but does not form distinct leaflets.
- Compound
The leaf blade is separated into separate leaflets. There are several ways in which the leaflets may be arranged on the rachis.
- Pinnate (odd): Leaflets are attached along the rachis; there is a terminal leaflet and therefore an odd number of leaflets.
- Pinnate (even): Leaflets are attached along the rachis; there is no terminal leaflet and therefore an even number of leaflets.
- Bipinnate: Leaflets that are further subdivided in a unipinnate arrangement.
- Tripinnate: Leaflets that are further subdivided in a bipinnate arrangement.
- Trifoliate: A compound leaf made up of three leaflets.
- Palmate/Digitate: A type of compound leaf in which the leaflets all originate from the same point, like the fingers from the palm of the hand.|
A way to distinguish simple leaves from compound leaves is to check for axillary buds. Only simple leaves would have an axillary bud. Pinnate leaves will not have them.
Leaf arrangement
- Alternate: One leaf attached at a node, arranged alternately on the stem.
- Opposite: A pair of leaves attached at a node, arranged oppositely.
- Whorled: Three or more leaves attached at a node, in a radial manner.
- Basal Rosette: Some plants keep their leaves in a tight rosette close to the ground, where the leaves all seem to radiate from a common point. This may be one stage in the life of the plant or it may spend its whole life in that form.
Leaf Shape
Leaves come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Leaf attachment
The point of attachment of a leaf to a stem.
Leaf margin
A leaf can be entire (one with a smooth edge) or it can be of the following types.
Inflorescence
The grouping or cluster of flowers on a branch or a network of branches.