Note: This is a project under development. The articles on this wiki are just being initiated and broadly incomplete. You can Help creating new pages.
Difference between revisions of "Pausinystalia johimbe - Yohimbe"
(→Photo Gallery) |
(→Photo Gallery) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
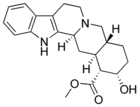
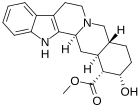
File:Yohimbine.png | File:Yohimbine.png | ||
File:Yohimbine structure.svg | File:Yohimbine structure.svg | ||
| − | + | Pau de cabinda.jpg | |
| + | |||
File:Lto-hmhm-yohimbetabletten.jpg | File:Lto-hmhm-yohimbetabletten.jpg | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 10:15, 29 May 2018
Yohimbe is a plant species native to western and central Africa. Extracts from yohimbe have been used in traditional medicine in West Africa as an aphrodisiac and have been marketed in developed countries as dietary supplements.
Contents
- 1 Uses
- 2 Parts Used
- 3 Chemical Composition
- 4 Common names
- 5 Properties
- 6 Habit
- 7 Identification
- 8 List of Ayurvedic medicine in which the herb is used
- 9 Where to get the saplings
- 10 Mode of Propagation
- 11 How to plant/cultivate
- 12 Commonly seen growing in areas
- 13 Photo Gallery
- 14 References
- 15 External Links
Uses
Erectile dysfunction, Depression, chest pain, exhaustion, blood pressure, diabetic nerve pain, Drowsiness, impotence, frigidity
Parts Used
Bark.
Chemical Composition
Yohimbe bark extract contains approximately 6% indole alkaloids, of which 10-15% is yohimbine. A 1995 chemical analysis of 26 commercial yohimbe products reported that most commercial yohimbe products contained virtually no yohimbine[1]
Common names
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Kannada | |
| Hindi | |
| Malayalam | |
| Tamil | |
| Telugu | |
| Marathi | NA |
| Gujarathi | NA |
| Punjabi | NA |
| Kashmiri | NA |
| Sanskrit | |
| English | Agrimony |
Properties
Reference: Dravya - Substance, Rasa - Taste, Guna - Qualities, Veerya - Potency, Vipaka - Post-digesion effect, Karma - Pharmacological activity, Prabhava - Therepeutics.
Dravya
Rasa
Tikta (Bitter), Kashaya (Astringent)
Guna
Laghu (Light), Ruksha (Dry), Tikshna (Sharp)
Veerya
Ushna (Hot)
Vipaka
Katu (Pungent)
Karma
Kapha, Vata
Prabhava
Habit
Identification
Leaf
| Kind | Shape | Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Simple | The leaves are divided into 3-6 toothed leaflets, with smaller leaflets in between |
Flower
| Type | Size | Color and composition | Stamen | More information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unisexual | 2-4cm long | Yellow | 5-20 | Flowers Season is June - August |
Fruit
| Type | Size | Mass | Appearance | Seeds | More information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7–10 mm | clearly grooved lengthwise, Lowest hooked hairs aligned towards crown | {{{6}}} |
Other features
List of Ayurvedic medicine in which the herb is used
- Vishatinduka Taila as root juice extract
Where to get the saplings
Mode of Propagation
How to plant/cultivate
A plant of the humid, lowland tropics, where it is found at elevations up to 500 metres[2]
Commonly seen growing in areas
Forest area, Closed canopy forest, Coastal forest.
Photo Gallery
References
External Links
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Erectile dysfunction
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Depression
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat chest pain
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat exhaustion
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat blood pressure
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat diabetic nerve pain
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat Drowsiness
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat impotence
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat frigidity
- Herbs with Bark used in medicine
- Herbs with common name in English
- Habit - Evergreen Tree
- Index of Plants which can be propagated by Seeds
- Herbs that are commonly seen in the region of Forest area
- Herbs that are commonly seen in the region of Closed canopy forest
- Herbs that are commonly seen in the region of Coastal forest
- Herbs