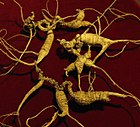
Note: This is a project under development. The articles on this wiki are just being initiated and broadly incomplete. You can Help creating new pages.
Difference between revisions of "Panax quinquefolius - American ginseng"
m (Prabhakar moved page American ginseng to American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius)) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{stub}} | ||
| + | |||
[[File:Marathonginsengberry.jpg|thumb|right|''American ginseng'', ''Panacis quinquefolis'']] | [[File:Marathonginsengberry.jpg|thumb|right|''American ginseng'', ''Panacis quinquefolis'']] | ||
| − | '''Panacis quinquefolis''' | + | '''Panacis quinquefolis''' is a herbaceous perennial plant in the ivy family, commonly used as Chinese or Herbal medicine. An extract is sold as Cold-fX. It is native to eastern North America, though it is also cultivated in places such as China. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Uses== | ||
| + | {{Uses|migraines}}, {{Uses|headaches}}, {{Uses|vomiting}}, {{Uses|piles}}, {{Uses|burning sensation}}, {{Uses|perspiration problems}}, {{Uses|burning sensation in the vagina}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Parts Used== | ||
| + | {{Parts Used|Root tubers}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Chemical Composition== | ||
| + | Atisine, Aconitine, Atisenol, Atidine, Hetisine, Hetisinone, Banzolheteratisine, Histidine, F-dihydroatisine, Heteratisine and Several diterpene alkaloids such aheterophyllin, heterophyllisin, heterophyllidine, and hetidine.<ref name="chemical composition"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Common names== | ||
| + | {{Common names|kn=Ativisa|ml=Ativisam|sa=Ativisha|ta=Atividyam|te=Ati visa|hi=Atis|en=Indian Atees}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Habit== | ||
| + | {{Habit|Herb}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Identification== | ||
| + | ===Leaf=== | ||
| + | {{Leaf|glabrous|sessile|The leaves are variable in shape and size}}.<ref name="Leaf"/> | ||
| − | == | + | ===Flower=== |
| + | {{Flower|Unisexual|2-4cm long|white–violet|10-18|Flowers are Large, hooded and occur in slender racemes or lax leafy panicles. Corolla is hairy. Carpels are five in number}} | ||
| − | + | ===Fruit=== | |
| − | + | {{Fruit||7–10 mm (0.28–0.4 in.) long pome||s|}} | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ===Other features=== |
| − | * '' | + | ==List of Ayurvedic medicine in which the herb is used== |
| + | * [[Vishatinduka Taila]] as ''root juice extract'' | ||
| − | == | + | ==Where to get the saplings== |
| + | ==Mode of Propagation== | ||
| + | {{Propagation|Seeds}}, {{Propagation|Tuber segment}}. | ||
| − | + | ==How to plant/cultivate== | |
| − | + | The more common species of Aconitum are generally those cultivated in gardens, especially hybrids. They typically thrive in well-drained evenly moist garden soils like the related hellebores and delphiniums, and can grow in the shade of trees.<ref name="How to plant/cultivate"/> | |
| − | |||
| − | <ref name=" | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Commonly seen growing in areas== |
| − | + | {{Commonly seen|western Himalayas}}, {{Commonly seen|open woodland}}, {{Commonly seen|moisty soil area}}. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Photo Gallery== | |
| + | <gallery class="left" caption="" widths="140px" heights="140px"> | ||
| + | File:Americanginseng.jpg|American ginseng in human figure | ||
| + | File:MonkGinsengGarden.jpg|Under wooden shade, American ginseng in late fall at Monk Garden in Wisconsin | ||
| + | File:American-ginseng-with-fruit.jpg|A picture of the American Ginseng plant with fruit. | ||
| + | File:Marathonginsengberry.jpg|American ginseng berries are ripe by late fall in Wisconsin. | ||
| + | File:Drawn image of fruit and leaf.jpg|A drawn image of the fruit and leaf of the American Ginseng plant | ||
| + | File:Drawn image.png|A drawn image of the American ginseng plants leaves | ||
| + | File:American Ginseng.jpg|American wild ginseng root (Panax quinquefolius). This is a very old specimen, showing over 60 growth scars. | ||
| + | File:American Ginseng 3.jpg|American wild ginseng root (Panax quinquefolius). Very old roots, ranging from 40–60 growth scars. | ||
| + | File:American Ginseng 1.jpg|American wild ginseng root (Panax quinquefolius). This is a very old specimen, showing over 60 growth scars. | ||
| + | File:American Ginseng 2.jpg|American wild ginseng root (Panax quinquefolius). Very old roots, ranging from 40–65 growth scars. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 12:08, 6 April 2018
Panacis quinquefolis is a herbaceous perennial plant in the ivy family, commonly used as Chinese or Herbal medicine. An extract is sold as Cold-fX. It is native to eastern North America, though it is also cultivated in places such as China.
Contents
Uses
migraines, headaches, vomiting, piles, burning sensation, perspiration problems, burning sensation in the vagina.
Parts Used
Chemical Composition
Atisine, Aconitine, Atisenol, Atidine, Hetisine, Hetisinone, Banzolheteratisine, Histidine, F-dihydroatisine, Heteratisine and Several diterpene alkaloids such aheterophyllin, heterophyllisin, heterophyllidine, and hetidine.[1]
Common names
| Language | Common name |
|---|---|
| Kannada | Ativisa |
| Hindi | Atis |
| Malayalam | Ativisam |
| Tamil | Atividyam |
| Telugu | Ati visa |
| Marathi | NA |
| Gujarathi | NA |
| Punjabi | NA |
| Kashmiri | NA |
| Sanskrit | Ativisha |
| English | Indian Atees |
Habit
Identification
Leaf
| Kind | Shape | Feature |
|---|---|---|
| glabrous | sessile | The leaves are variable in shape and size |
.[2]
Flower
| Type | Size | Color and composition | Stamen | More information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unisexual | 2-4cm long | white–violet | 10-18 | Flowers are Large, hooded and occur in slender racemes or lax leafy panicles. Corolla is hairy. Carpels are five in number |
Fruit
| Type | Size | Mass | Appearance | Seeds | More information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7–10 mm (0.28–0.4 in.) long pome | s | {{{6}}} |
Other features
List of Ayurvedic medicine in which the herb is used
- Vishatinduka Taila as root juice extract
Where to get the saplings
Mode of Propagation
How to plant/cultivate
The more common species of Aconitum are generally those cultivated in gardens, especially hybrids. They typically thrive in well-drained evenly moist garden soils like the related hellebores and delphiniums, and can grow in the shade of trees.[3]
Commonly seen growing in areas
western Himalayas, open woodland, moisty soil area.
Photo Gallery
- Pages that are stubs
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat migraines
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat headaches
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat vomiting
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat piles
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat burning sensation
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat perspiration problems
- Ayurvedic Herbs known to be helpful to treat burning sensation in the vagina
- Herbs with Root tubers used in medicine
- Herbs with common name in Kannada
- Herbs with common name in Hindi
- Herbs with common name in Malayalam
- Herbs with common name in Tamil
- Herbs with common name in Telugu
- Herbs with common name in Sanskrit
- Herbs with common name in English
- Habit - Herb
- Index of Plants which can be propagated by Seeds
- Index of Plants which can be propagated by Tuber segment
- Herbs that are commonly seen in the region of western Himalayas
- Herbs that are commonly seen in the region of open woodland
- Herbs that are commonly seen in the region of moisty soil area
- Pages with reference errors